As China drops restrictions on QFII/RQFII investment quotas and the US Federal Reserve cuts interest rates, China’s capital market is likely to benefit and it is more convenient for overseas investors to participate in China’s domestic financial markets.
China is the largest and most influential emerging market in the world, with strong economic growth and rising global status. If you live in China, it’s a good chance to invest and make a fortune.
Today, we are going to introduce you some policies which encourage foreigners to invest and improve your financial condition in China.
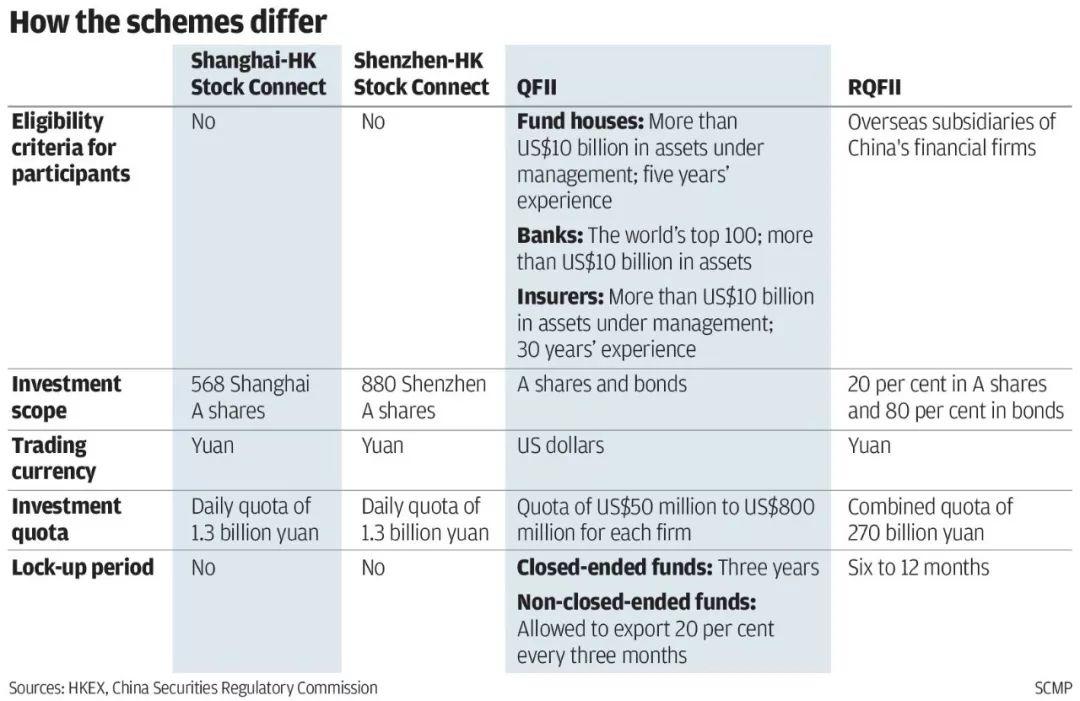
On Sept 10, the SAFE announced that it will abolish the investment quota restrictions for the Qualified Foreign Institutional Investors (QFII) and Renminbi Qualified Foreign Institutional Investors (RQFII) to boost financial reforms and opening-up.
QFII, set up in 2002, lets foreign funds invest onshore in China’s yuan-denominated A-shares.
The PQFII program, introduced in 2011, gives investors access to offshore RMB to buy mainland-traded stocks.
These two investment schemes are a major part of China’s strategy to open its capital markets to global investors. More than 400 institutional investors from 31 countries and regions have used them to access China’s capital markets.
In an effort to open up China’s financial markets, the QFII program had undergone several developments in recent years, including:
-
Removal of relevant lock-up periods;
-
Allowing foreign exchange hedging of securities held by QFIIs in China;
-
Doubling the total quota from $150 million to $300million.
In SAFE’s press conference, it was announced that the relevant regulations will be revised soon. In other words,
-
Foreign investors that have obtained the relevant qualifications approved by the CSRC will only need to go through a registration process.
-
Domestic custodian banks will be able to assist foreign investors with such registration in order to obtain a registration certificate issued by SAFE.
-
Post-registration, investors will be able to open special fund accounts with the domestic custodian banks to handle the follow-up remittance of funds and exchange business.
Additionally, the jurisdictional limit on the RQFII program will be lifted and will be qualified foreign institutions worldwide while it was available only to financial institutions in 19 countries and regions before.
As the world’s second largest economy fights slowing growth at home and a damaging trade war with the U.S., China lifts some restrictions on foreign investment in the financial sector.
China will remove shareholding limits on foreign ownership in 2020. The involving sectors include:
Foreign investors will also be encouraged to set up wealth management firms, currency brokerages and pension management companies.
Foreign-owned credit rating agencies will also be allowed to evaluate a greater number of bond and debt types.
Allowance of A-Shares Trading
In order to further open up China’s capital market, qualified foreign individual investors from 62 countries and regions are allowed to trade domestic A-shares through local brokers since Sept 15, 2018.
As the China Securities Depository and Clearing Corporation (CSDC) said on its website, the updated regulations:
-
Expand the investor base;
-
Introduce more liquidity;
-
Improve the structure of the securities market.
Under the regulations, foreigners matching the following criteria can set up A-share trading accounts:
-
Foreigners with a permanent China residence card.
-
Foreign employees of listed A-share companies who currently live in China or abroad, as long as participating in the company’s equity incentives.
-
Foreigners working in China, regardless of whether they have obtained a permanent residence ID card or not.
-
Foreigners who have established foreign-invested joint-stock companies in China which are listed on the A-share market.
Click the link to know more about it!
Since the first foreign-invested company entered China about 40 years ago, China’s economic development has been closely connected with foreign investors.
In 2018, FDI into China reached 138.3 billion dollars, 151 times that of 1983 and representing an average annual rate of 15.4 percent.
Over 960,000 foreign-invested enterprises had been set up in China by the end of last year, with the accumulated foreign direct investment exceeding 2.1 trillion dollars.
China has been making consistent efforts to optimize its business environment and embrace investors worldwide and will create a stable, transparent, predictable and fair market environment in the future.
The country will set up 6 new pilot free trade zones to bring the total number to 18, which serve as pioneers to test new forms of:
- Foreign investment management,
- Trade facilitation, and
- Transformation of government functions.
The country will also lift the investment quota limit for approved foreign investors to boost financial reform and opening up.
Share to let your friends know!
SOURCE | XINHUA NET/SCMP